Materiality and Stakeholder Communication

Materiality and Stakeholder Communication
Procedure of Materiality Analysis
Every year, CTCI conducts regular investigations and analyses of materiality, adhering to GRI 3: Material Topics 2021, which is a part of the GRI Universal Standards 2021. This process also incorporates the concept of Double Materiality as recommended by the European Financial Reporting Advisory Group (EFRAG), establishing an analytical framework that encompasses both impact materiality and financial materiality. In terms of impact significance, CTCI integrates the methodologies for assessing economic, environmental, and human (human rights) impacts developed by organizations such as the Value Balancing Alliance (VBA), Harvard Business School’s Impact-Weighted Accounts research initiative, and the London Benchmarking Group (LBG), so as to establish a systematic evaluation process that involves monetized and non-monetized approaches. The material issues related to the analysis process and definition of materiality for 2024 have been verified by SGS Taiwan using the AA 1000 Assurance Standards (Assurance Standards v3) Type II, and have received a high level of trust.

Stage 1: Identifying Communication Objects and Issues
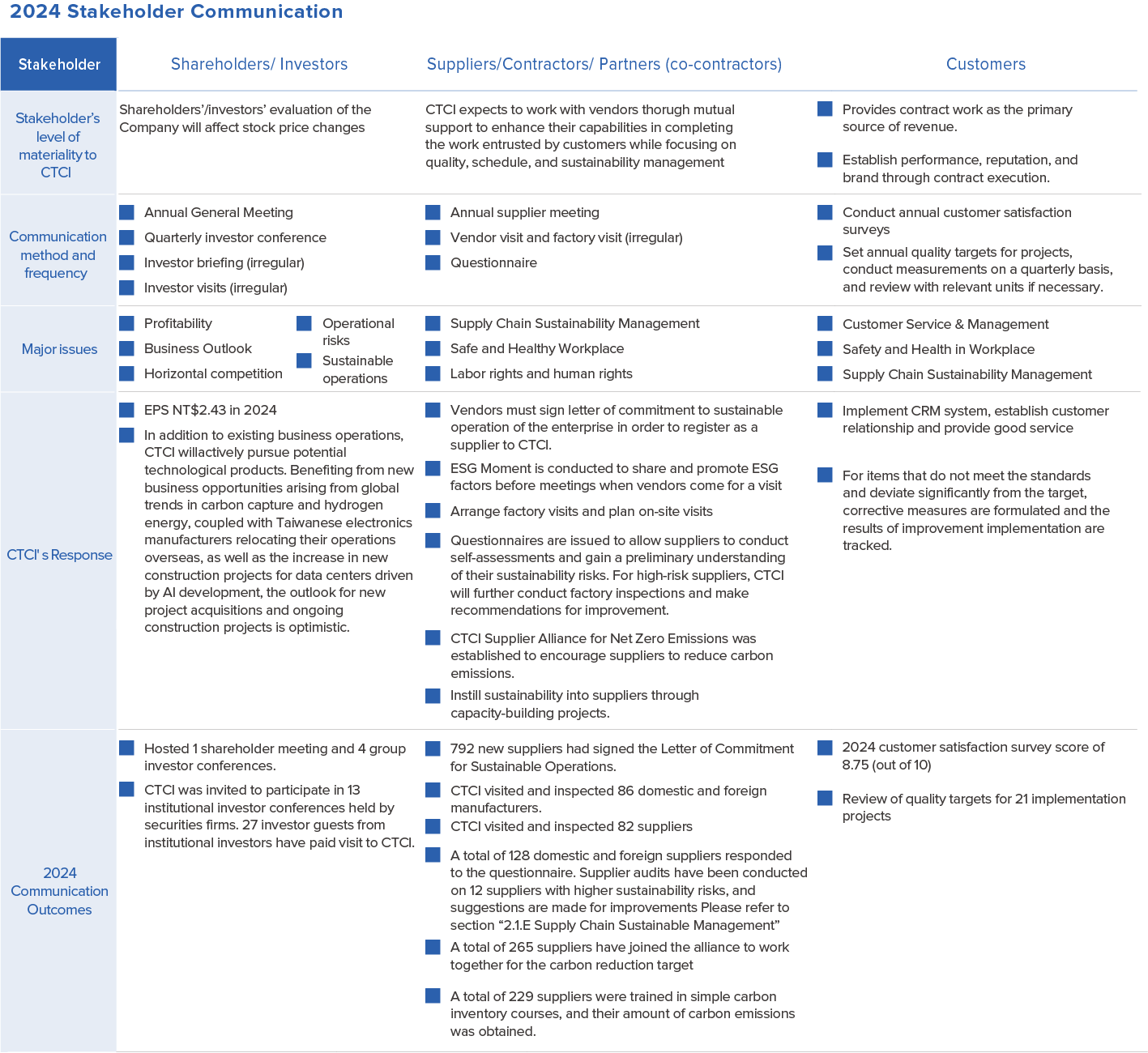
CTCI refers to the five key principles of the AA1000 Stakeholder Engagement Standard to identify six categories of stakeholders, which include shareholders/investors, suppliers/contractors/partners, customers, employees, media, and the community/government/experts/associations.
In response to the growing concerns of internal and external stakeholders regarding sustainability issues, as well as the rapid changes in international trends, CTCI annually references the GRI Standards, the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD), and the issues of interest to investment institutions such as S&P Global ESG, MSCI ESG Ratings, and CDP, to dynamically adjust its sustainability topics. In 2024, a total of 19 ESG topics relevant to the operations of CTCI have been collected.

Stage 2: Analysis of Materiality Questionnaire
● Stakeholder Concern Level: CTCI has referenced the five key principles of the AA1000 Stakeholder Engagement Standard, taking into account the dependency, responsibilities, concerns, influence, and diverse perspectives of each category of stakeholders in determining their priority for communication. As a result, six categories of stakeholders were identified, and they were invited to complete a questionnaire. A total of 843 responses were collected, including 588 from employees, 11 from shareholders/investors, 163 from suppliers/contractors/partners, 17 from customers, 10 from media representatives, and 54 from community/government/expert scholars/associations.
● CTCI Operational Impact: Measure the impact of sustainability issues on CTCI’s operations, including revenue, customer satisfaction, operational risk, employee loyalty, and brand image, while 27 senior executives jointly determine the importance of each sustainability issue to CTCI’s operations.
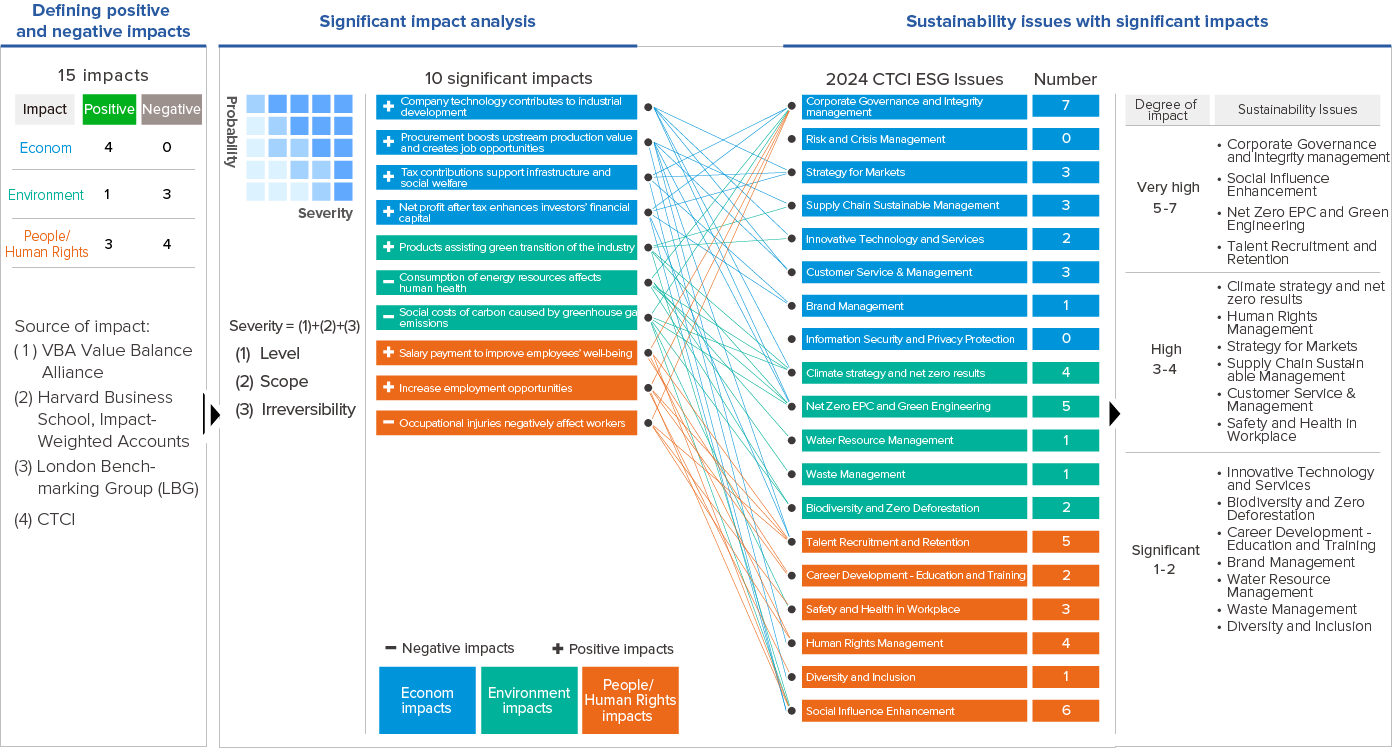
● Sustainability Impact Assessment: CTCI adopts a mixed evaluation approach that includes both monetized and non-monetized methods. In the non-monetized approach, it integrates frameworks from organizations such as the Value Balancing Alliance (VBA), Harvard Business School’s Impact-Weighted Accounts research initiative, and the London Benchmarking Group (LBG). This assessment is conducted from the perspectives of economic, environmental, and human (human rights) impacts, with input from 25 executives and employees who identify significant impacts and sustainability issues from positive and negative, actual and potential, irreparable, and value chain viewpoints. Regarding the monetized assessment, CTCI conducts regular annual sustainability impact valuations, utilizing a Profit & Loss perspective to measure the positive (benefits) and negative (costs) impacts on human well-being and socio-economic conditions resulting directly or indirectly from value chain activities.

CTCI’s Impact Assessment Process - Non-Monetary
In response to each external sustainable development impact related to the economy, environment, and human rights, 25 executives and project managers from CTCI identified significant impact items and affected sustainability issues. Ultimately, 10 items were identified as having significant impacts that have occurred or may occur in the future for CTCI. These include 4 items related to economic impacts, 3 items related to environmental impacts, and 3 items related to human rights impacts.

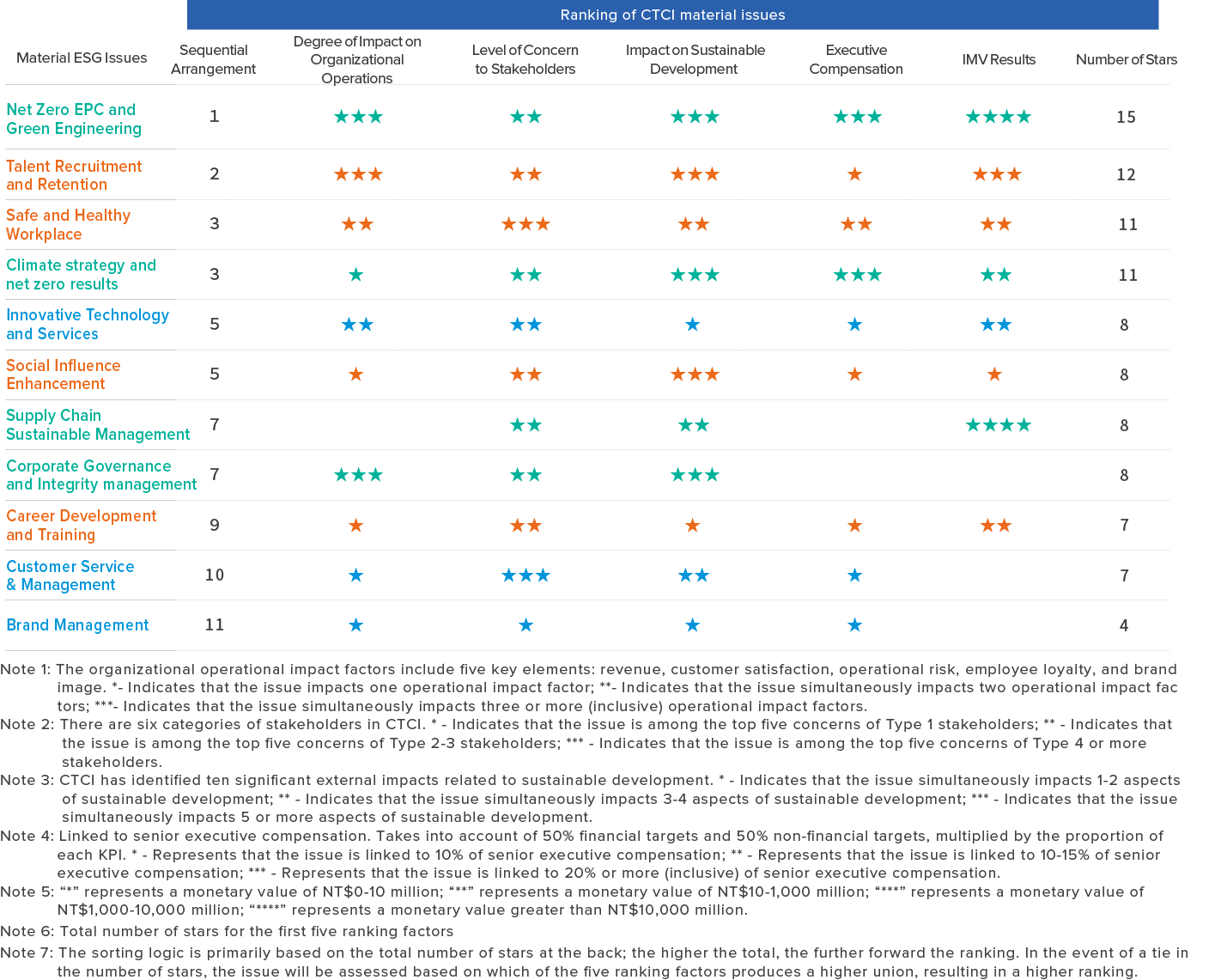
Stage 3: Selection and Confirmation of Major Issues
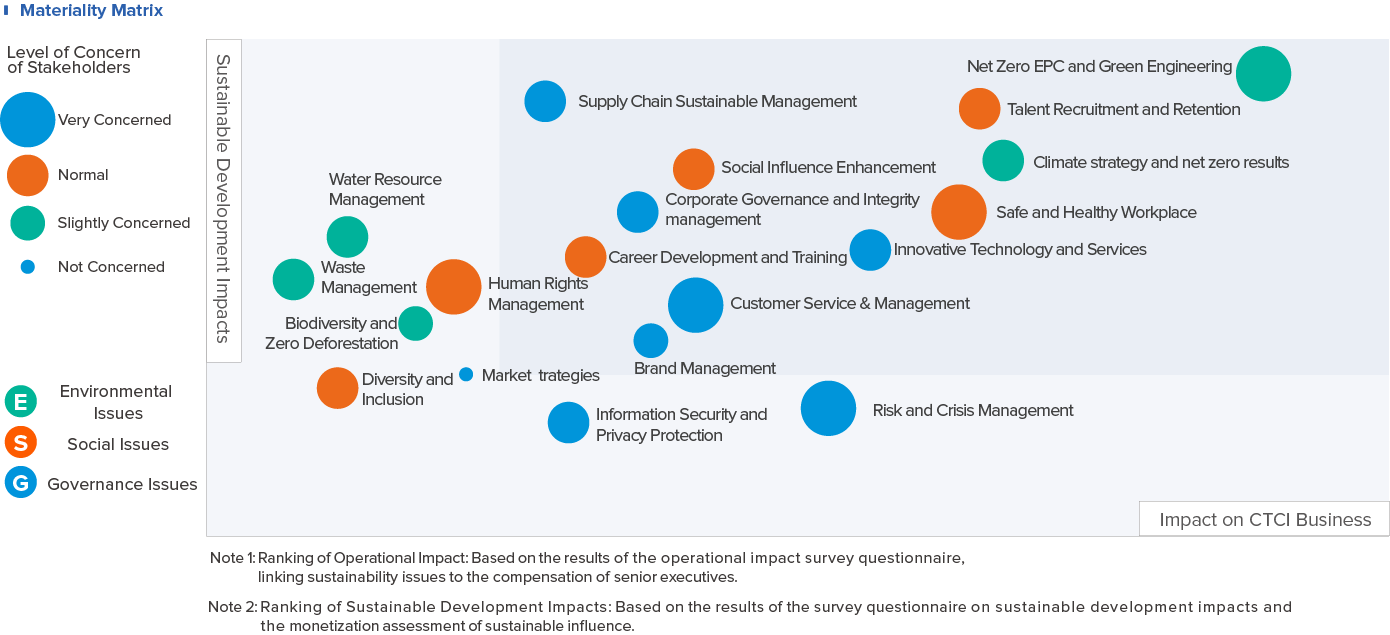
Based on the analysis results of three questionnaires, issues of concern to stakeholders and which have an impact on operations and external sustainable development were identified. Additionally, reference was made to 11 significant issues from the previous year whose long-term goals were set. The ESG issues linked to senior executive compensation were also considered in the selection of significant issues for 2024. The Board of Directors confirmed the final decision on 11 major issues: “Corporate Governance and Integrity Management,” “Sustainable Supply Chain Management,” “Innovative Technology and Services,” “Customer Service and Management,” “Brand Management,” “Climate Strategy and Net Zero Results,” “Net Zero EPC and Green Engineering,” “Talent Recruitment and Retention,” “Career Development and Training,” “Safe and Healthy Workplace,” and “Social Influence Enhancement.”

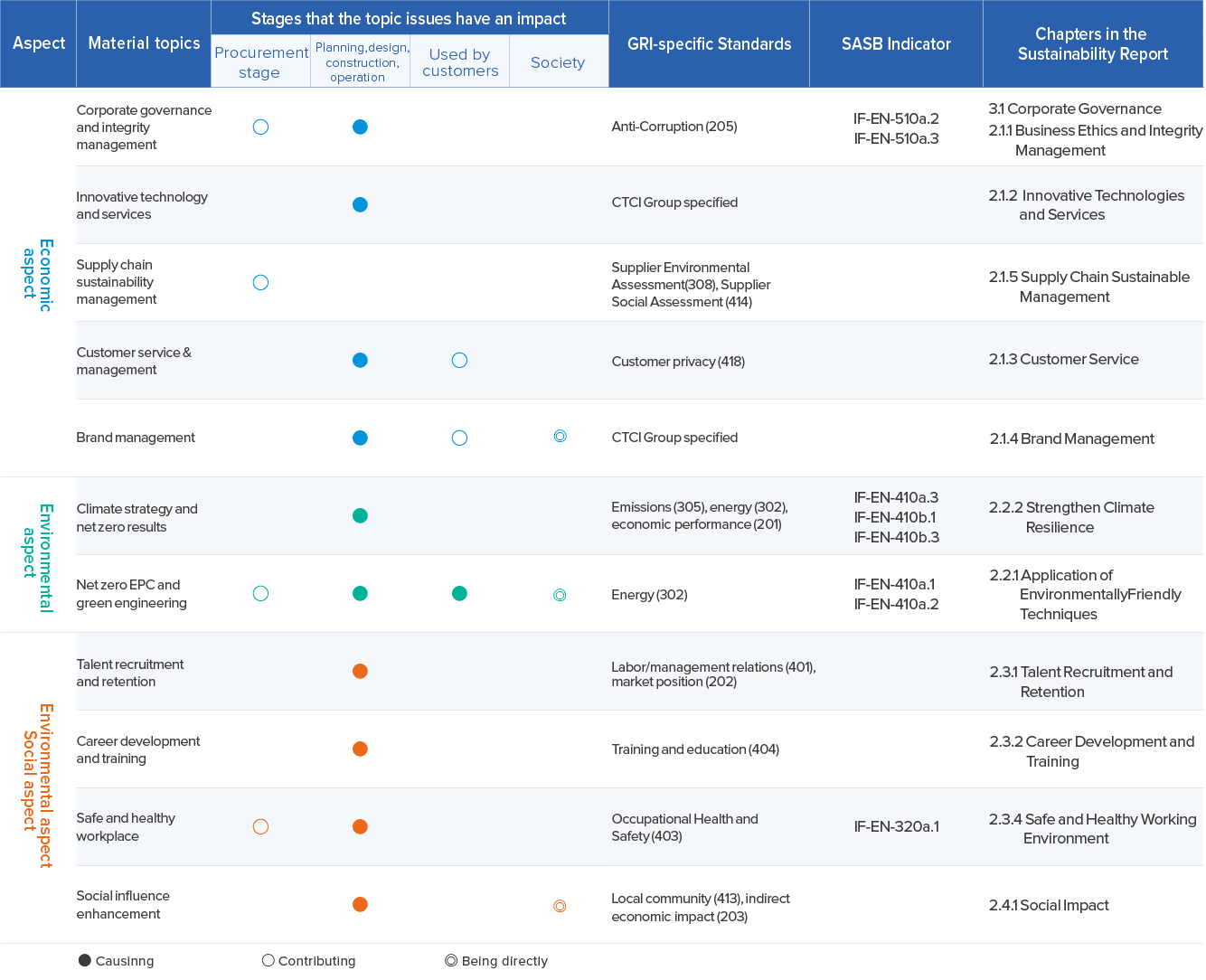
Stage 4: Boundaries of Major Issues
After confirming 11 significant issues, we identified 11 material themes related to CTCI in accordance with the GRI standards (13 themes are GRI themes, and 2 pertain specifically to CTCI). Following the reporting requirements of the standards, we collected and disclosed internal information, data, and management policies, and systematically examined the impact of these significant issues across the value chain of CTCI. This includes the upstream procurement phase, the planning, design, construction, and operation phases within CTCI, the downstream customer use phase, and the effects on societal boundaries. The material themes identified by CTCI are integrated with the risk assessment operations initiated by the Risk Management & Control Office every six months. Through risk identification, analysis, and evaluation, as well as subsequent risk mitigation, management, and monitoring, the implementation of Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) is ensured.

Materiality Matrix
2024 Stakeholder Communication
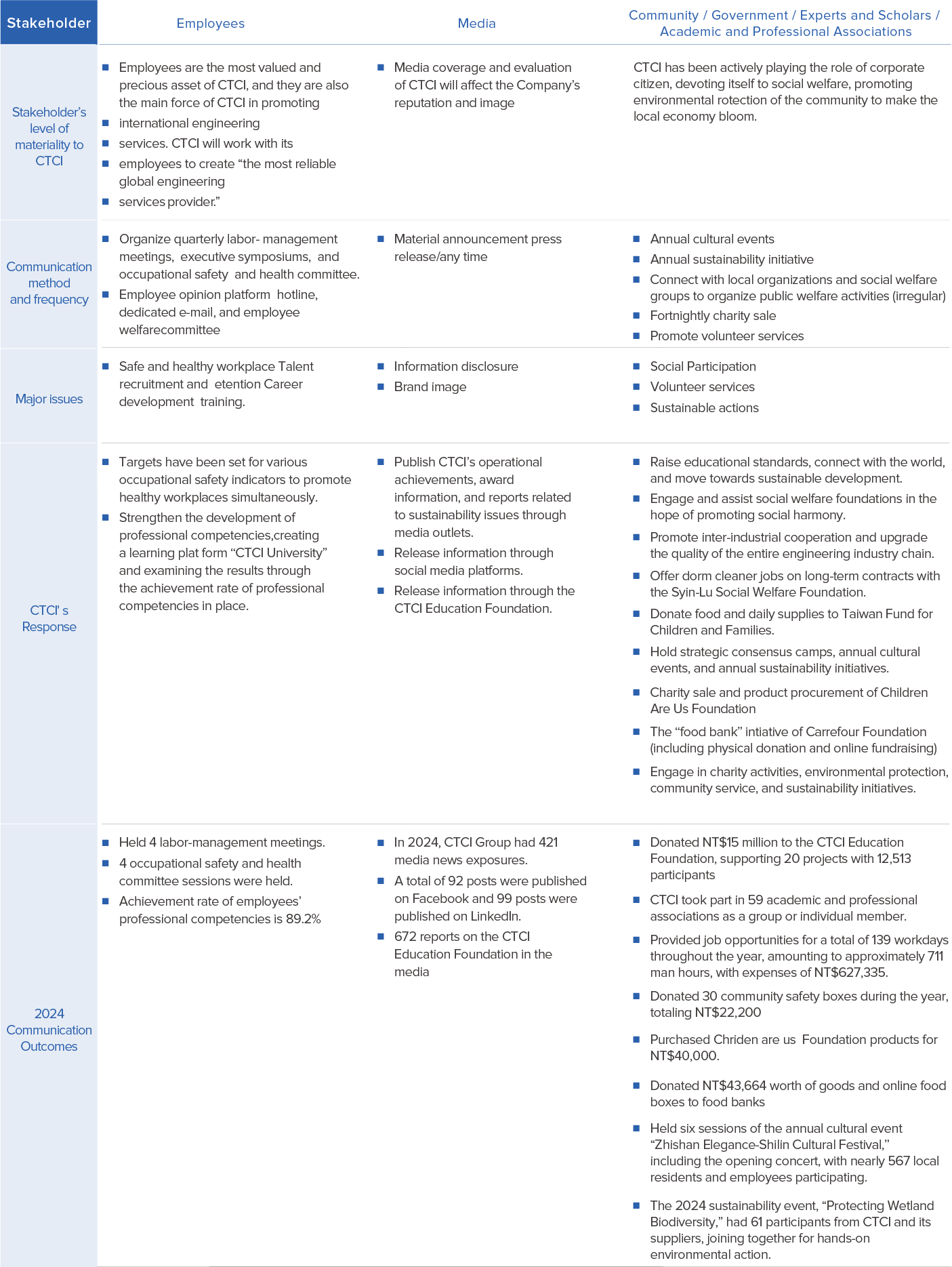
Stakeholder communication channels